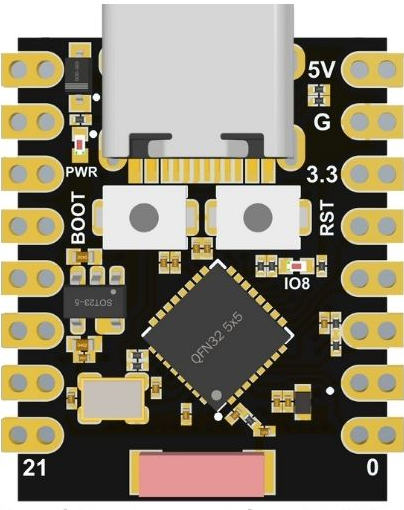
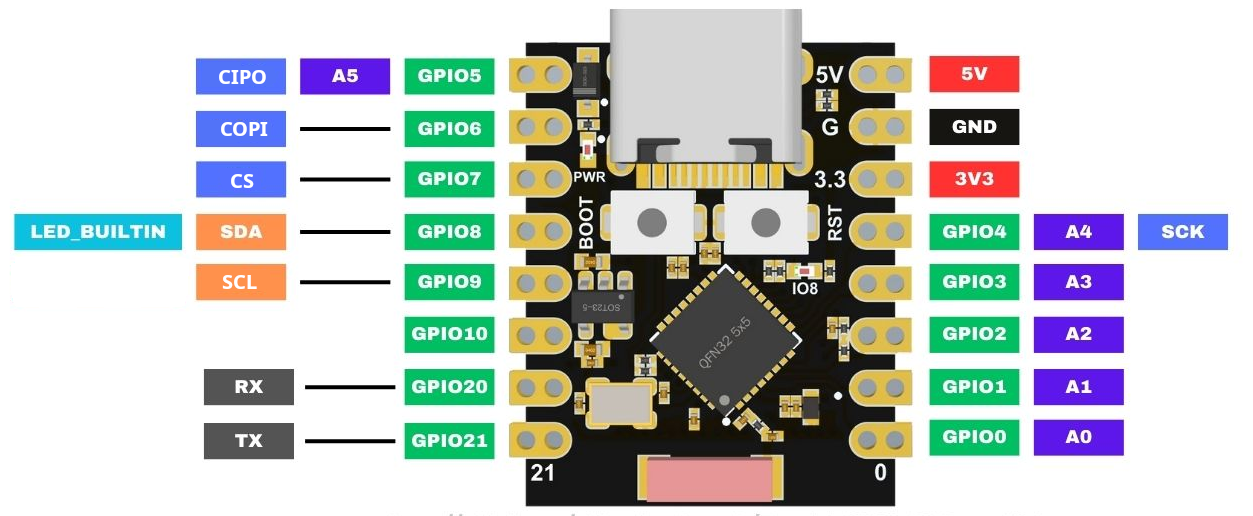
Der ESP32-C3 Super Mini hat insgesamt 18 Pins, 3 dienen der Stromversorgung, es bleiben 15 Pins, die mehrfach belegt sind.
Er verfügt über Bluetooth und WiFi.
Board installieren
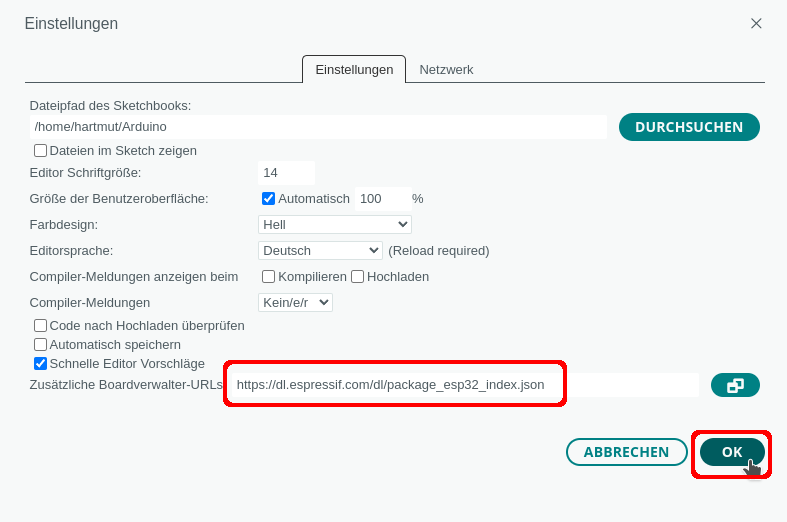
Trage unter Datei -> Einstellungen eine zusätzliche Boardverwalter-URL ein:
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json
Board auswählen
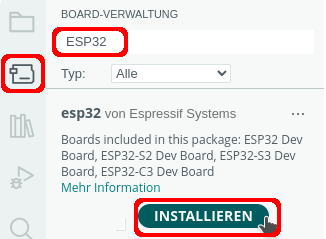
- Icon für den Boardverwalter anklicken oder Werkzeuge-> Board -> Boardverwalter
- nach ESP32 suchen
- Board installieren
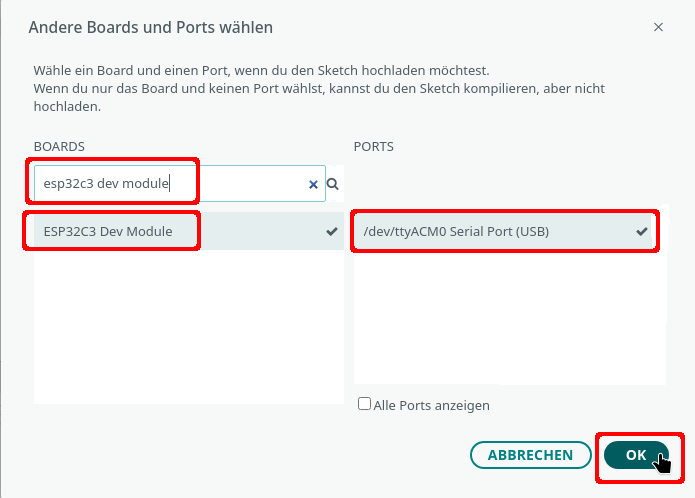
Wenn der ESP32-C3 nicht automatisch erkannt wurde, klicke auf "Wähle ein anderes Board und einen anderen Port" und suche nach esp32c6. Je nach Betriebssystem wird der USB-Port eine andere Bezeichnung haben.
Seriellen Monitor einschalten
Der Serielle Monitor steht erst nach einer Änderung der Konfiguration zur Verfügung:

LED
Auf dem Board ist an Pin 8 eine blaue LED verbaut.
void setup()
{
pinMode(8, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(8, HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
delay(1000);
}Pinbelegung
I²C
⇒Info

I²C-Pins
9 -> SCL
8 -> SDA
Beispiel 0,96 Zoll OLED
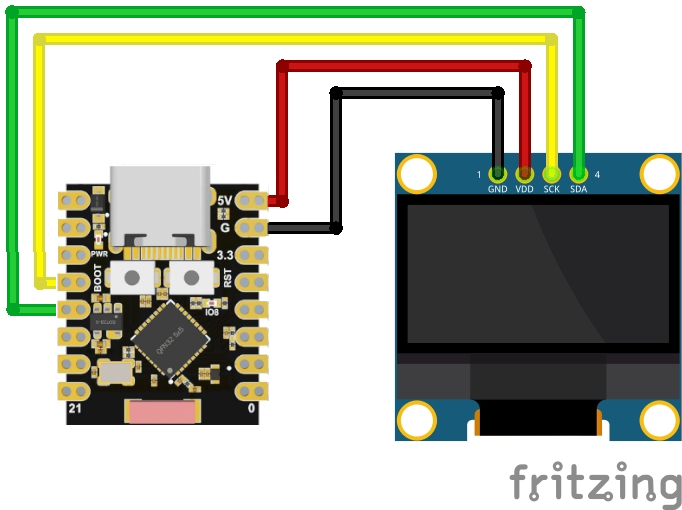
Benötigte Bibliothek installieren
#include "U8g2lib.h"
// 0,96 Zoll SSD1306
U8G2_SSD1306_128X64_NONAME_F_HW_I2C oled(U8G2_R0);
// Bildschirmgröße
int BildschirmBreite = oled.getDisplayWidth();
int BildschirmHoehe = oled.getDisplayHeight();
// Smiley XBM erstellt mit GIMP
#define SmileyBreite 46
#define SmileyHoehe 45
static unsigned char Smiley[] =
{
0x00, 0x00, 0xfe, 0x1f, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xc0, 0xff, 0xff, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0xf0, 0x07, 0xf8, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0xfc, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x0f, 0x00,
0x00, 0x3e, 0x00, 0x00, 0x1f, 0x00, 0x80, 0x0f, 0x00, 0x00, 0x7c, 0x00,
0xc0, 0x07, 0x00, 0x00, 0xf8, 0x00, 0xe0, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0xe0, 0x01,
0xf0, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x03, 0x70, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x80, 0x03,
0x38, 0x7e, 0x00, 0x80, 0x1f, 0x07, 0x38, 0xff, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x07,
0x9c, 0xff, 0x01, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x0e, 0x9c, 0xe7, 0x01, 0xc0, 0x39, 0x0e,
0x8e, 0xc3, 0x01, 0xc0, 0x30, 0x1c, 0x8e, 0xe3, 0x01, 0xc0, 0x31, 0x1c,
0x86, 0xf7, 0x01, 0xc0, 0x3b, 0x18, 0x87, 0xff, 0x01, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0x38,
0x07, 0xff, 0x00, 0x80, 0x3f, 0x38, 0x03, 0x7e, 0x00, 0x80, 0x1f, 0x30,
0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30,
0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30,
0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x30,
0x07, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x38, 0x07, 0x20, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01, 0x38,
0x06, 0x70, 0x00, 0x80, 0x03, 0x18, 0x0e, 0xf0, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x01, 0x1c,
0x0e, 0xe0, 0x03, 0xf0, 0x01, 0x1c, 0x1c, 0xc0, 0x3f, 0xfc, 0x00, 0x0e,
0x1c, 0x80, 0xff, 0x7f, 0x00, 0x0e, 0x38, 0x00, 0xfc, 0x1f, 0x00, 0x07,
0x38, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x03, 0x00, 0x07, 0x70, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x80, 0x03,
0xf0, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x03, 0xe0, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0xe0, 0x01,
0xc0, 0x07, 0x00, 0x00, 0xf8, 0x00, 0x80, 0x0f, 0x00, 0x00, 0x7c, 0x00,
0x00, 0x3e, 0x00, 0x00, 0x1f, 0x00, 0x00, 0xfc, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x0f, 0x00,
0x00, 0xf0, 0x07, 0xf8, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0xc0, 0xff, 0xff, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0xfe, 0x1f, 0x00, 0x00
};
// Schneemann XBM erstellt mit GIMP
#define SchneemannBreite 28
#define SchneemannHoehe 62
static unsigned char Schneemann[] =
{
0x00, 0xf0, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0xfc, 0x07, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0e, 0x06, 0x00,
0x00, 0x06, 0x0c, 0x00, 0x00, 0x02, 0x08, 0x00, 0x00, 0x03, 0x18, 0x00,
0x00, 0x03, 0x18, 0x00, 0x00, 0x03, 0x18, 0x00, 0x00, 0x03, 0x38, 0x00,
0xe0, 0xff, 0xff, 0x03, 0x00, 0xfe, 0x0f, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0f, 0x1e, 0x00,
0x80, 0x03, 0x1c, 0x00, 0x80, 0x01, 0x38, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x19, 0x37, 0x00,
0xc0, 0x1c, 0x37, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x18, 0x27, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x00, 0x20, 0x00,
0xc0, 0x08, 0x21, 0x00, 0xc0, 0xf9, 0x31, 0x00, 0xc0, 0xf1, 0x38, 0x00,
0x80, 0x03, 0x38, 0x00, 0x80, 0x07, 0x1c, 0x00, 0x00, 0x1f, 0x0f, 0x00,
0x00, 0xfc, 0x07, 0x00, 0x00, 0xfc, 0x03, 0x04, 0x00, 0xff, 0x0f, 0x06,
0x80, 0x07, 0x1e, 0x06, 0xc0, 0x03, 0x3c, 0x03, 0xe0, 0x00, 0x70, 0x03,
0xf0, 0x00, 0xf0, 0x01, 0x70, 0x00, 0xe0, 0x00, 0x38, 0x00, 0xc0, 0x01,
0x38, 0xf0, 0xc0, 0x01, 0x18, 0xf0, 0xe0, 0x01, 0x18, 0xf0, 0xb0, 0x01,
0x0c, 0x70, 0x30, 0x03, 0x0c, 0x00, 0x18, 0x03, 0x0c, 0x00, 0x18, 0x03,
0x0e, 0x00, 0x08, 0x07, 0x06, 0x00, 0x0f, 0x06, 0x06, 0x00, 0x0f, 0x06,
0x06, 0x30, 0x06, 0x06, 0x06, 0x70, 0x00, 0x06, 0x06, 0xf0, 0x00, 0x06,
0x06, 0xf0, 0x00, 0x06, 0x0e, 0x60, 0x00, 0x07, 0x0c, 0x00, 0x00, 0x03,
0x0c, 0x00, 0x00, 0x03, 0x0c, 0x00, 0x00, 0x03, 0x0c, 0x00, 0x00, 0x03,
0x18, 0x00, 0x80, 0x01, 0x38, 0x60, 0xc0, 0x01, 0x38, 0xf0, 0xc0, 0x01,
0x78, 0xf0, 0xe0, 0x00, 0xf0, 0xf0, 0xf0, 0x00, 0xf0, 0x00, 0x70, 0x00,
0xe0, 0x03, 0x7c, 0x00, 0xe0, 0x07, 0x3e, 0x00, 0xe0, 0xff, 0x3f, 0x00,
0xc0, 0xff, 0x1f, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
};
void setup()
{
// Zufallsgenerator starten
randomSeed(A0);
// Display starten
oled.begin();
// Kontrast maximal 255
oled.setContrast(200);
}
void loop()
{
// Farbe weiß
oled.setDrawColor(1);
// Smiley
oled.clearBuffer();
oled.drawXBM(40, 10, SmileyBreite, SmileyHoehe, Smiley);
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// Schneemann
oled.clearBuffer();
oled.drawXBM(50, 1, SchneemannBreite, SchneemannHoehe, Schneemann);
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// Pixelmuster
oled.clearBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++)
{
int x = random(1, BildschirmBreite);
int y = random(1, BildschirmHoehe);
oled.drawPixel(x, y);
}
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
oled.setFont(u8g2_font_unifont_t_symbols);
// Text horizontal
oled.clearBuffer();
oled.setFontDirection(0);
oled.setCursor(2, BildschirmHoehe / 2);
oled.print("Text");
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// Text 90 Grad gedreht
oled.clearBuffer();
oled.setFontDirection(1);
oled.setCursor(BildschirmBreite / 2, 2);
oled.print("Text");
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// Text 180 Grad gedreht
oled.clearBuffer();
oled.setFontDirection(2);
oled.setCursor(BildschirmBreite - 2, BildschirmHoehe / 2);
oled.print("Text");
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// Text 270 Grad gedreht
oled.clearBuffer();
oled.setFontDirection(3);
oled.setCursor(BildschirmBreite / 2, BildschirmHoehe - 2);
oled.print("Text");
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// Kreise
oled.clearBuffer();
for (int i = 2; i < BildschirmHoehe / 2; i += 3)
{
oled.drawCircle(BildschirmBreite / 2, BildschirmHoehe / 2, i);
}
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// Rahmen
oled.clearBuffer();
for (int i = 2; i < BildschirmHoehe; i += 4)
{
oled.drawFrame(0, 0, i, i);
}
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// vertikale Linie
oled.clearBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < BildschirmBreite; i += 4)
{
oled.drawVLine(i, 0, BildschirmBreite - 1);
}
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// horizontale Linie
oled.clearBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < BildschirmHoehe; i += 4)
{
oled.drawHLine(0, i, BildschirmBreite - 1);
}
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// ausgefüllte Kreise
oled.clearBuffer();
int Radius = 5;
int StartX = 10;
int StartY = 10;
while (StartX < BildschirmBreite - Radius)
{
for (int i = StartY; i < BildschirmBreite - Radius; i += 20)
{
oled.drawDisc(StartX, i, Radius);
}
StartX += 10;
}
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
// Linien
oled.clearBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < BildschirmBreite; i += 5)
{
oled.drawLine(0, i, 128, 64);
}
for (int i = BildschirmBreite; i > 0; i -= 5)
{
oled.drawLine(BildschirmBreite, i, 0, 0);
}
oled.sendBuffer();
delay(2000);
}SPI
⇒Info
SPI-Pins
5 -> CIPO (MISO)
6 -> COPI (MOSI)
7-> CS
4 -> SCK/CLK
Beispiel: Anschluss eines runden TFTs

gelb -> 2 (RST)
weiß -> 7 (CS)
grün -> 3 (DC)
blau -> 6 (SDA)
braun -> 4 (SCL)
schwarz -> GND
rot -> 5V
schwarz -> GND
Benötigte Bibliothek

#include "Adafruit_GFX.h"
#include "Adafruit_GC9A01A.h"
#define TFT_RST 2
#define TFT_DC 3
#define TFT_CS 7
// Farben
#define SCHWARZ 0x0000
#define WEISS 0xFFFF
#define BLAU 0x001F
#define ROT 0xF800
#define GRUEN 0x07E0
#define CYAN 0x07FF
#define MAGENTA 0xF81F
#define GELB 0xFFE0
#define BRAUN 0x9A60
#define GRAU 0x7BEF
#define GRUENGELB 0xB7E0
#define DUNKELCYAN 0x03EF
#define ORANGE 0xFDA0
#define PINK 0xFE19
#define BORDEAUX 0xA000
#define HELLBLAU 0x867D
#define VIOLETT 0x915C
#define SILBER 0xC618
#define GOLD 0xFEA0
Adafruit_GC9A01A tft(TFT_CS, TFT_DC);
void setup()
{
// Zufallsgenerator starten
randomSeed(analogRead(A0));
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(500);
Serial.println("Bildschirm: " + String(tft.height()) + " x " + String(tft.width()));
// TFT starten
tft.begin();
// Rotation anpassen
tft.setRotation(2);
// schwarzer Hintergrund
tft.fillScreen(SCHWARZ);
// interne Textdarstellung
tft.setTextSize(3);
tft.setCursor(30, 50);
tft.setTextColor(BLAU);
tft.print("Text");
delay(500);
tft.setTextSize(4);
tft.setCursor(30, 80);
tft.setTextColor(GRUEN);
tft.print("Text");
delay(2000);
// zufällige Pixel
tft.fillScreen(SCHWARZ);
for (int i = 0; i < 700; i++)
{
int PixelX = random(1, tft.width());
int PixelY = random(1, tft.height());
tft.drawPixel(PixelX, PixelY, tft.color565(random(255),random(255),random(255)));
delay(5);
}
delay(2000);
// Kreise vom Mittelpunkt zeichnen
tft.fillScreen(SCHWARZ);
for (int i = 1; i < tft.width() / 2; i+=5)
{
tft.drawCircle(tft.width() / 2, tft.height() / 2, tft.width() / 2 - i, tft.color565(random(255),random(255),random(255)));
delay(50);
}
delay(2000);
for (int i = 1; i < tft.width() / 2; i+=5)
{
tft.drawCircle(tft.width() / 2, tft.height() / 2, tft.width() / 2 - i, SCHWARZ);
delay(50);
}
delay(2000);
// Kreise vom Mittelpunkt zeichnen
tft.fillScreen(SCHWARZ);
for (int i = 1; i < tft.width() / 2; i+=10)
{
tft.fillCircle(tft.width() / 2, tft.height() / 2, tft.width() / 2 - i, tft.color565(random(255),random(255),random(255)));
delay(50);
}
delay(2000);
/*
alle 30° Linie vom Mittelpunkt zeichnen
120 = Radius des TFTs (240/2)
90 = PI/4 (Viertelkreis)
DEG_TO_RAD (0.0174532925) -> Winkel in Bogenmaß umrechnen
es ensteht ein Dreieck mit einem Rechten Winkel
-> Winkelfunktionen sin/cos anwenden
*/
tft.fillScreen(SCHWARZ);
for (int i = 0; i < 360; i += 30)
{
float PosX = cos((i - 90) * DEG_TO_RAD) * 120;
float PosY = sin((i - 90) * DEG_TO_RAD) * 120;
int PunktX = PosX + 120;
int PunktY = PosY + 120;
tft.drawLine(120, 120, PosX + 120, PosY + 120, WEISS);
}
delay(2000);
}
void loop()
{
// nichts zu tun, das Programm
// läuft nur einmal
}Analoge Pins
Die Auflösung des ADC-Wandlers kann zwischen 9-Bit (0 - 511), 10 Bit (0 - 1023), 11 Bit (0 - 2047) und 12 Bit (0 - 4095) Die Standardeinstellung ist 12 Bit. Die Anweisung analogReadResolution() beeinflusst den ADC-Wandler.

Analoge Pins
4 (SPI)
3
2
1
0
Beispiel:
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
analogReadResolution(10);
}
void loop()
{
Serial.println("ADC-Wert: " + String(analogRead(0)));
delay(200);
}Digitale Pins
Alle Pins können digitale Signale verarbeiten:
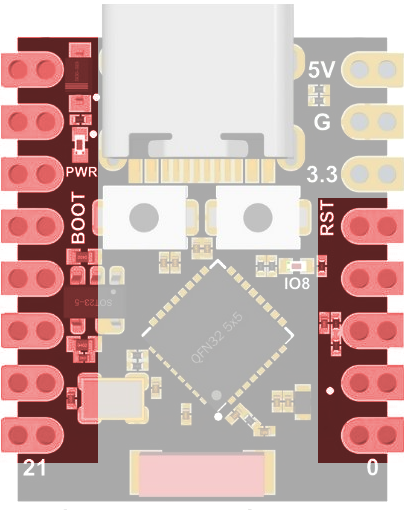
Zeit mit der Bibliothek time.h anzeigen
ESP32-Mikrocontroller können mit der Standardbibliothek time.h Datum und Zeit anzeigen.
Beispiel: ⇒Anzeige von Datum und Zeit auf einem OLED-Display

#include "WiFi.h"
#include "time.h"
char Router[] = "Router_SSID";
char Passwort[] = "xxxxxxxx";
// NTP-Server aus dem Pool
#define Zeitserver "de.pool.ntp.org"
/*
Liste der Zeitzonen
https://github.com/nayarsystems/posix_tz_db/blob/master/zones.csv
Zeitzone CET = Central European Time -1 -> 1 Stunde zurück
CEST = Central European Summer Time von
M3 = März, 5.0 = Sonntag 5. Woche, 02 = 2 Uhr
bis M10 = Oktober, 5.0 = Sonntag 5. Woche 03 = 3 Uhr
*/
#define Zeitzone "CET-1CEST,M3.5.0/02,M10.5.0/03"
// time_t enthält die Anzahl der Sekunden seit dem 1.1.1970 0 Uhr
time_t aktuelleZeit;
/*
Struktur tm
tm_hour -> Stunde: 0 bis 23
tm_min -> Minuten: 0 bis 59
tm_sec -> Sekunden 0 bis 59
tm_mday -> Tag 1 bis 31
tm_wday -> Wochentag (0 = Sonntag, 6 = Samstag)
tm_mon -> Monat: 0 (Januar) bis 11 (Dezember)
tm_year -> Jahre seit 1900
tm_yday -> vergangene Tage seit 1. Januar des Jahres
tm_isdst -> Wert > 0 = Sommerzeit (dst = daylight saving time)
*/
tm Zeit;
WiFiServer Server(80);
WiFiClient Client;
void setup()
{
// Zeitzone: Parameter für die zu ermittelnde Zeit
configTzTime(Zeitzone, Zeitserver);
Serial.begin(9600);
// auf serielle Verbindung warten
while (!Serial);
delay(1000);
// WiFi starten
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.begin(Router, Passwort);
Serial.println("------------------------");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED)
{
delay(200);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Verbunden mit ");
Serial.println(Router);
Serial.print("IP über DHCP: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void loop()
{
// aktuelle Zeit holen
time(&aktuelleZeit);
// localtime_r -> Zeit in die lokale Zeitzone setzen
localtime_r(&aktuelleZeit, &Zeit);
Serial.println("------------------------");
// es kann bis zu 30 Sekunden dauern
// bis die Zeit ermittelt wird
// Name des Wochentages 0-6
switch (Zeit.tm_wday)
{
case 0:
Serial.print("Sonntag");
break;
case 1:
Serial.print("Montag");
break;
case 2:
Serial.print("Dienstag");
break;
case 3:
Serial.print("Mittwoch");
break;
case 4:
Serial.print("Donnerstag");
break;
case 5:
Serial.print("Freitag");
break;
case 6:
Serial.print("Samstag");
break;
}
Serial.print(",");
if (Zeit.tm_mday < 10) Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(Zeit.tm_mday);
Serial.print(".");
// Monat: führende 0 ergänzen
// Zählung beginnt mit 0 -> +1
if ((Zeit.tm_mon + 1) < 10) Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(Zeit.tm_mon + 1);
Serial.print(".");
// Anzahl Jahre seit 1900
Serial.print(Zeit.tm_year + 1900);
Serial.print(" ");
// Stunde: wenn Stunde < 10 -> 0 davor setzen
if (Zeit.tm_hour < 10) Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(Zeit.tm_hour);
Serial.print(":");
// Minuten
if (Zeit.tm_min < 10) Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(Zeit.tm_min);
Serial.print(":");
// Sekunden
if (Zeit.tm_sec < 10) Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(Zeit.tm_sec);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Tage seit dem 1.1. " + String(Zeit.tm_yday));
// Normalzeit/Sommerzeit
if(Zeit.tm_isdst > 0) Serial.println("MESZ = Mitteleuropäische Sommerzeit");
else Serial.println("MEZ = Mitteleuropäische Zeit");
delay(5000);
}Webserver
Beispiel
Das Programm zeigt im Browser 6 Zufallszahlen an.
Im Seriellen Monitor wird die mit DHCP ermittelte IP des ESP32-C3 angezeigt.

Diese Adresse musst du in einem Browser deiner Wahl eingeben.

#include "WiFi.h"
#include "WebServer.h"
// SSID und Passwort des Routers
char Router[] = "Router_SSID";
char Passwort[] = "xxxxxxxx";
WebServer Server(80);
// Minimum und Maximum der Zufallszahlen
int Minimum = 1;
int Maximum = 49;
// statischeIP = false -> IP-Adresse über DHCP vergeben
// statischeIP = true -> statische IP festlegen
bool statischeIP = false;
// ip und gateway müssen an das lokale Netz angepasst werden
IPAddress ip(192, 168, 1, 100);
IPAddress gateway(192, 168, 1, 1);
IPAddress subnet(255, 255, 255, 0);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
// auf serielle Verbindung warten
while (!Serial);
delay(1000);
// WiFi starten
WiFi.begin(Router, Passwort);
// statische IP vergeben
if (statischeIP)
{
WiFi.config(ip, gateway, subnet);
Serial.print("Verbunden mit ");
Serial.println(Router);
// IP anzeigen
Serial.print("Statische IP: ");
}
// IP über DHCP ermitteln
else
{
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED)
{
delay(200);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Verbunden mit ");
Serial.println(Router);
Serial.print("IP über DHCP: ");
}
// IP anzeigen
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
// Zufallsgenerator mit dem Signal an A0 starten
randomSeed(analogRead(A0));
Server.begin();
Server.on("/", SeiteBauen);
}
void loop()
{
Server.handleClient();
}
void SeiteBauen()
{
// Seite zusammenbauen
// Kopf der HTML-Seite: aktualisierung alle 60 Sekunden
// kann angepasst werden
String Nachricht = "<head><meta http-equiv=\"refresh\" content=\"60\"></head>";
Nachricht += "<h1>Zufallszahlen</h1>";
Nachricht += "<hr>";
// Zufallszahlen anzeigen
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
int Zahl = random(Minimum, Maximum);
Nachricht += String(Zahl) + " ";
}
Nachricht += "<hr>";
// Nachricht senden -> Seite anzeigen
Server.send(200, "text/html", Nachricht);
}